Grain Sorghum
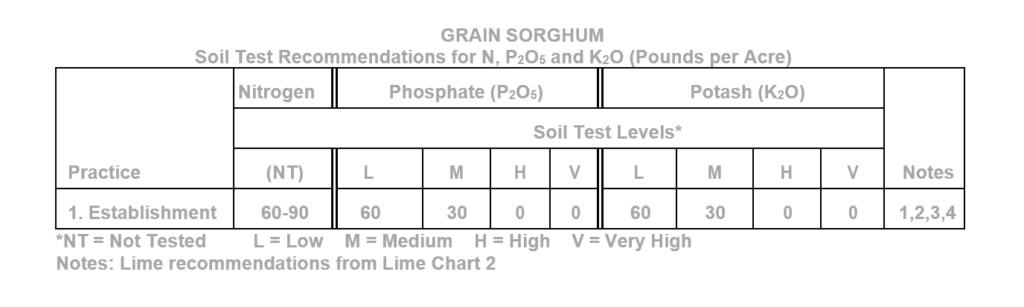
- Response to the higher rate of nitrogen would most likely occur when grain sorghum follows a non-legume, is grown no-till, or is grown on soils with restricted drainage or having textures with more clay than silty clay loam.
- Reduce N rate by 60 to 80 pounds per acre following a well-established single-species winter cover crop of crimson clover or hairy vetch that has reached early bloom stage.
- On soils having a coarse textured subsoil, 10 pounds of sulfur per acre as part of the fertilizer blend may benefit yield, especially where deficiency symptoms have been observed in the past or where plant tissue tests have suggested sulfur deficiency.
- When boron tests less than .8 lbs/acre apply 1.0 lb of boron per acre annually. Follow up with another soil test in two years. (Note 4 is used only when the boron test indicates a need for boron.)





