Corn Silage
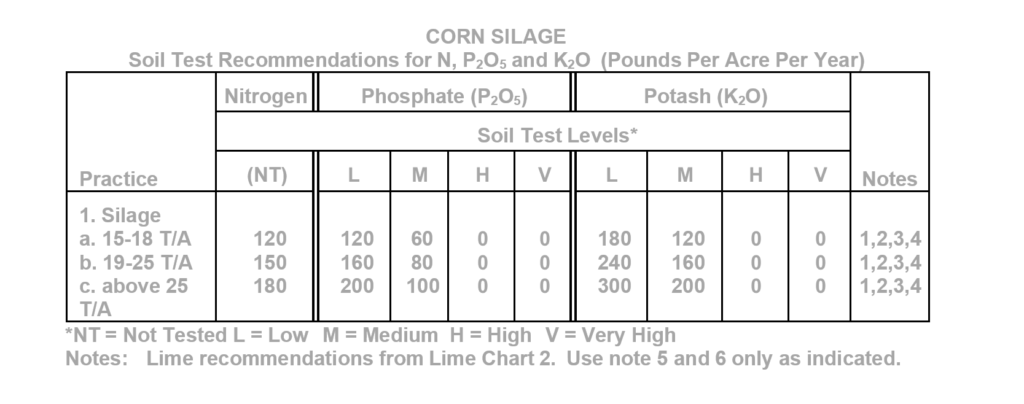
- Banding a portion or all of the phosphate and potash two inches to the side and below the seed level may result in increased yields on soils testing low in either or both phosphorus and potassium. For soils testing medium or higher, either banding or broadcasting are effective methods of If fertilizer is placed directly with the seed, do not apply more than 30 pounds per acre of nitrogen or nitrogen plus potash to prevent seedling injury and loss of stand.
- Split applications of nitrogen may be beneficial when nitrogen rates are greater than 120 pounds per acre.
- If nitrogen sources containing urea are not incorporated, some loss of nitrogen may occur, without the use of a urease inhibitor, if applied to moist soils followed by three or more days of rapidly drying conditions without rainfall.
- Reduce N rate by 60 to 80 pounds per acre following a winter cover crop of crimson clover or hairy vetch that has reached early bloom stage. Use Note 5 and 6 only as Indicated in the last sentence of the note.
- Apply five pounds of zinc (approximately 15 pounds zinc sulfate) per acre just prior to [Note 5 is used only when the zinc test indicates a need for zinc].
- If zinc was not tested, apply five pounds of zinc (approximately 15 pounds zinc sulfate) per acre when soil pH is 6.1 or above and phosphorus is high or anytime lime is applied or anywhere zinc deficiencies were observed the previous year. [Note 6 is used for the following counties when the zinc test is not requested: Bedford, Cannon, Coffee, Cumberland, Davidson, DeKalb, Fentress, Franklin, Giles, Grundy, Jackson, Lincoln, Macon, Marshall, Maury, Moore, Morgan, Overton, Pickett, Putnam, Robertson, Smith, Sumner, Trousdale, Warren, Williamson and Wilson].





